The Transition from HBM2 to HBM3: What You Need to Know
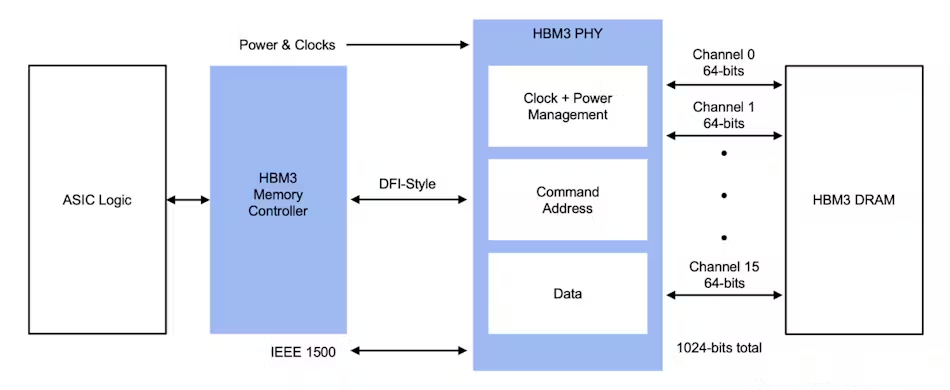
In the rapidly evolving world of high-performance computing, memory technologies play a crucial role in driving advancements. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) has emerged as a key player in this space, with the transition from HBM2 to HBM3 representing a significant leap forward. This blog post will delve into the details of this transition, exploring the improvements HBM3 brings over its predecessor, the potential impact on various industries, and what the future might hold.
Understanding HBM: A Brief Overview
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) is a high-speed memory interface designed to provide increased bandwidth and reduced power consumption compared to traditional memory technologies like DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM. HBM achieves this by stacking memory chips vertically and connecting them using an interposer with a high-speed interface. This design allows for a significant increase in memory bandwidth while also minimizing latency and power consumption.
HBM2 was a significant advancement over the original HBM standard, offering increased bandwidth and improved performance. It became widely adopted in applications requiring high memory bandwidth, such as high-end graphics cards, data center accelerators, and high-performance computing (HPC) systems.
Key Improvements from HBM2 to HBM3
The transition from HBM2 to HBM3 brings several notable improvements, designed to address the growing demands of modern computing applications:
1. Increased Bandwidth: HBM3 offers a substantial increase in memory bandwidth compared to HBM2. While HBM2 provides a peak bandwidth of up to 256 GB/s per stack, HBM3 can achieve peak bandwidths of up to 819 GB/s per stack. This increase is achieved through improvements in data rates and more efficient memory operations.
2. Higher Capacity: HBM3 supports higher capacity per stack, allowing for greater overall memory capacity in a given footprint. This is particularly important for applications such as AI and machine learning, where large datasets need to be processed quickly.
3. Enhanced Power Efficiency: Despite the increase in performance, HBM3 is designed to be more power-efficient than HBM2. It achieves this through improved power management features and more efficient memory access patterns.
4. Improved Latency: HBM3 reduces latency compared to HBM2, which enhances overall system responsiveness and performance. This is crucial for applications that require real-time processing and quick data access.
5. Greater Reliability: HBM3 introduces features that enhance reliability and error correction, ensuring data integrity in critical applications. This includes improvements in on-die ECC (Error Correction Code) and better support for high-density configurations.
Implications of HBM3 in Different Industries
The advancements brought by HBM3 are set to have a profound impact across various industries:
1. High-Performance Computing (HPC): HPC systems, which rely on immense computational power and memory bandwidth, will benefit significantly from HBM3's increased bandwidth and capacity. This will enhance the performance of simulations, data analysis, and complex computations.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML workloads require fast access to large datasets. HBM3's higher bandwidth and capacity will accelerate training and inference processes, making it easier to develop and deploy advanced AI models.
3. Graphics and Gaming: In the graphics and gaming industry, HBM3 will enable more detailed and complex graphics rendering. This will enhance the gaming experience and enable the development of more sophisticated visual effects.
4. Data Centers: Data centers, which handle vast amounts of data and require efficient memory solutions, will benefit from HBM3's improved power efficiency and bandwidth. This can lead to more efficient data processing and lower operational costs.
5. Networking and Telecommunications: High-speed networking equipment and telecommunications infrastructure can leverage HBM3 to manage and process large volumes of data more effectively. This is crucial for supporting the increasing demands of modern communication networks.
Challenges and Considerations
While the transition to HBM3 brings many benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
1. Cost: HBM3 is expected to be more expensive than HBM2 due to its advanced technology and higher performance capabilities. This could impact the cost of devices that utilize HBM3 memory.
2. Integration: Incorporating HBM3 into existing systems may require redesigning components and interfaces. This could pose challenges for manufacturers and require significant engineering effort.
3. Market Adoption: The adoption of HBM3 will depend on how quickly manufacturers and industry players can integrate the technology into their products. The pace of adoption will vary across different sectors.
The Future of High Bandwidth Memory
As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate further developments in memory technology beyond HBM3. Innovations such as HBM4 and other emerging memory solutions may continue to push the boundaries of performance, capacity, and efficiency.
In conclusion, the transition from HBM2 to HBM3 represents a major step forward in high-performance memory technology. With its increased bandwidth, higher capacity, and improved efficiency, HBM3 is poised to drive significant advancements in various industries. As we move forward, it will be exciting to see how this technology evolves and what new possibilities it will unlock for the future of computing.
Stay tuned for more updates on emerging technologies and their impact on our digital world!
 Innovative-hub for VLSI
Technology
Innovative-hub for VLSI
Technology












